RBAC Auditing Guide
The PyPermission library comes with a number of review functions and visualization tools, allowing for custom auditing workflows out of the box.
Review functions
| Review Function | Description | API Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Subjects of a Role | Returns all Subjects assigned to a Role. Optional inclusion of descendant Roles. |
pypermission.RBAC.role.subjects |
| Roles of a Subject | Returns all Roles assigned to a Subject. Optional inclusion of ascendant Roles. |
pypermission.RBAC.subject.roles |
| Permissions of a Role | Collects all Permissions directly granted to a Role or inherited from ascendant Roles. |
pypermission.RBAC.role.permissions |
| Permissions of a Subject | Aggregates all Permissions available to a Subject through its assigned Roles. |
pypermission.RBAC.subject.permissions |
| Policies of a Role | Returns all Policies associated with a Role, including inherited ones if requested. |
pypermission.RBAC.role.policies |
| Policies of a Subject | Returns all Policies linked to a Subject via its assigned Roles. |
pypermission.RBAC.subject.policies |
| Actions on a Resource for a Role | Lists all Actions a Role may perform on a given ResourceType and ResourceID (including wildcard Permissions). |
pypermission.RBAC.role.actions_on_resource |
| Actions on a Resource for a Subject | Lists all Actions a Subject may perform on a given ResourceType and ResourceID based on its Roles. |
pypermission.RBAC.subject.actions_on_resource |
Advanced RBAC auditing
Install the util dependency group:
pip install 'PyPermission[util]'
With the util extra installed, PyPermission can load the RBAC state directly from the database and build a NetworkX DAG that reflects all Roles, Subjects and Permissions. The generated graph and Plotly visualization making it easier to spot misconfigurations.
Info
An existing database with PyPermission RBAC tables is required, but no running application instance is needed. The util functions bypass the standard PyPermission API and read the authorization state directly from the database.
Export the RBAC DAG with NetworkX
The role_dag function builds an nx.DiGraph representation of the RBAC system directly from the database. It can optionally be scoped to a set of root_roles, in which case only those Roles and their ascendants are included. Setting include_subjects adds Subject nodes derived from Members, while include_permissions adds Permission nodes derived from Policies.
import networkx as nx
from sqlalchemy.engine.base import Engine
from sqlalchemy.engine import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from pypermission.util.role import role_dag
engine = create_engine(URL_TO_DB, future=True)
db_factory = sessionmaker(bind=engine, autoflush=False, autocommit=False)
with db_factory.begin() as db:
dag: nx.DiGraph = role_dag(db=db)
Plot the RBAC DAG with Plotly
The plot_factory function takes the nx.DiGraph produced by role_dag, renders the RBAC structure as an interactive Plotly graph and writes it to an HTML file. The auto_open flag controls whether the generated file is opened in the browser immediately, while file_path specifies where the visualization is stored.
import networkx as nx
from sqlalchemy.engine.base import Engine
from sqlalchemy.engine import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from pypermission.util.role import role_dag
from pypermission.util.plot import plot_factory
engine = create_engine(URL_TO_DB, future=True)
db_factory = sessionmaker(bind=engine, autoflush=False, autocommit=False)
with db_factory.begin() as db:
dag: nx.DiGraph = role_dag(db=db)
plot_factory(dag=dag, auto_open=False, file_path="dag.html")
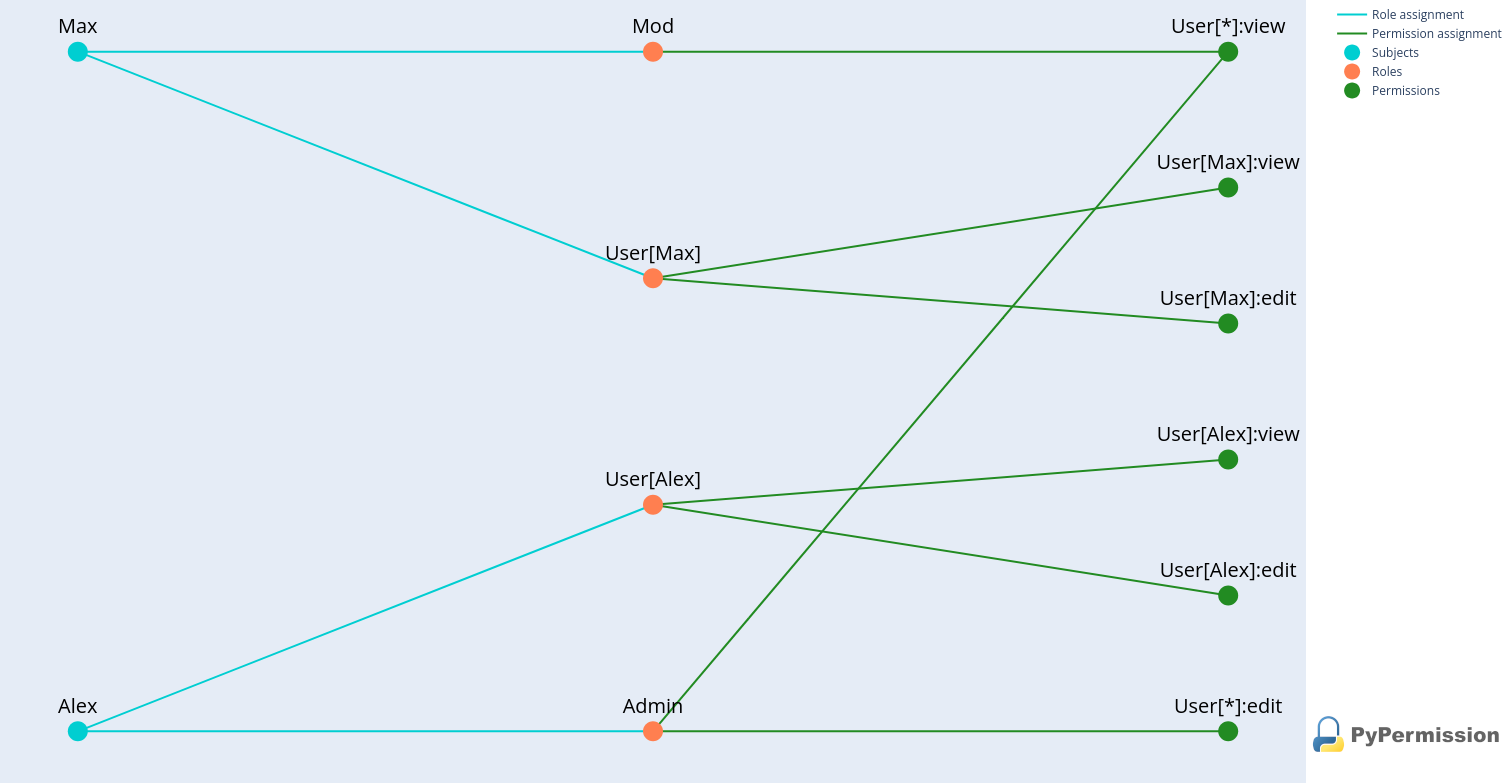 Auditing graph for RBAC in Python
Auditing graph for RBAC in Python